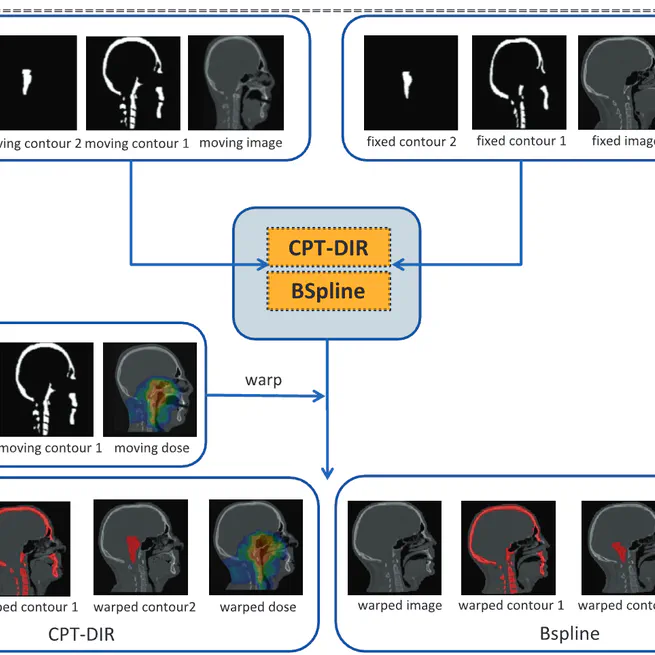
The integration of contour-informed regularization in CPT-DIR improved DIR accuracy, particularly in anatomically and dosimetrically relevant regions.
Jan 1, 2026
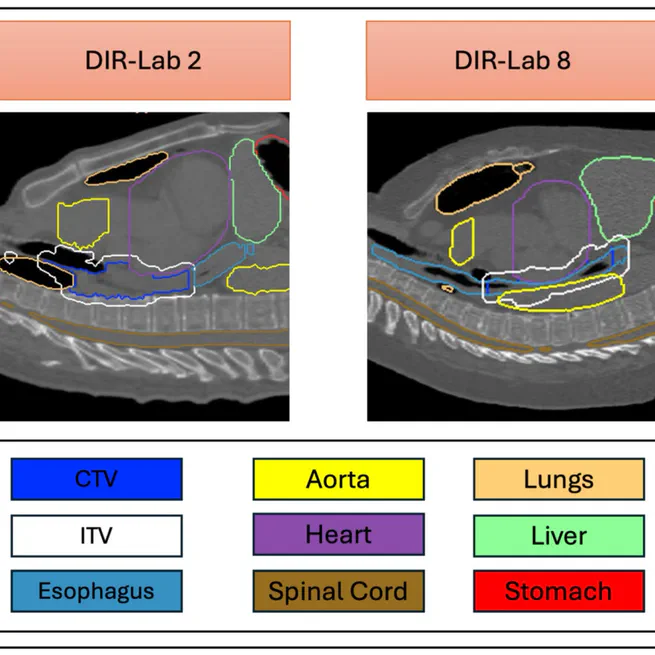
Protocol-based static 4DDC tended to overestimate target coverage robustness to respiratory motion. Although differences were minor in most cases, patients with large motion can have significant discrepancies, underscoring the importance of implementing dynamic 4DDC in PBS proton planning for esophageal cancer.
Jan 1, 2026
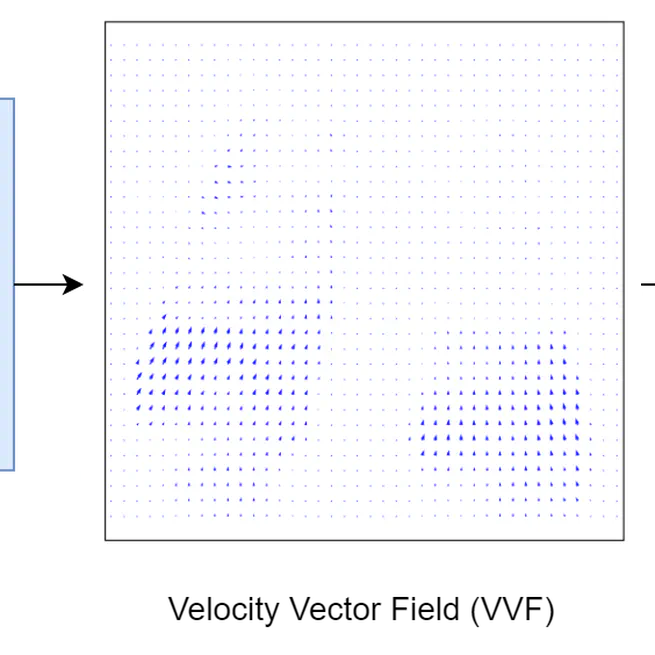
By leveraging the continuous representations, the CPT-DIR method enhances registration and interpolation accuracy, automation, and speed.
Dec 26, 2025
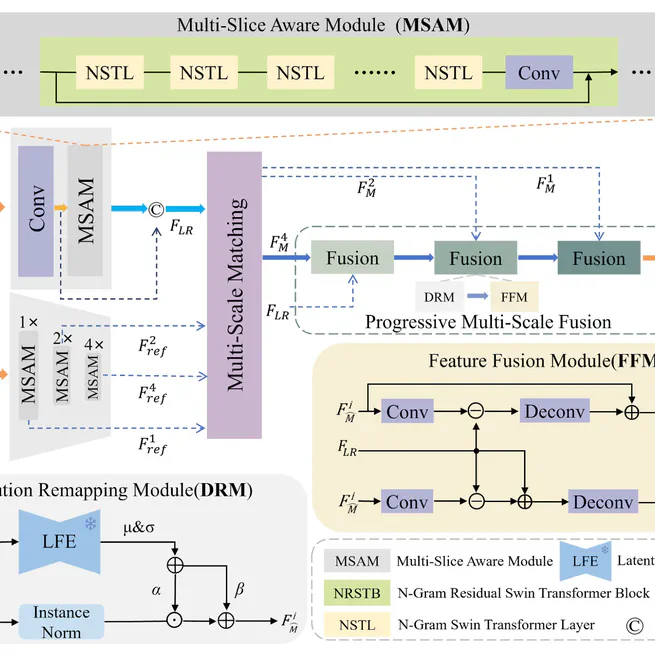
A Multi-Slice Aware Matching and Fusion (MSAMF) network for brain MRI super-resolution that utilizes multi-slice reference images through multi-scale matching and fusion mechanisms to generate high-quality super-resolution images.
Oct 1, 2025
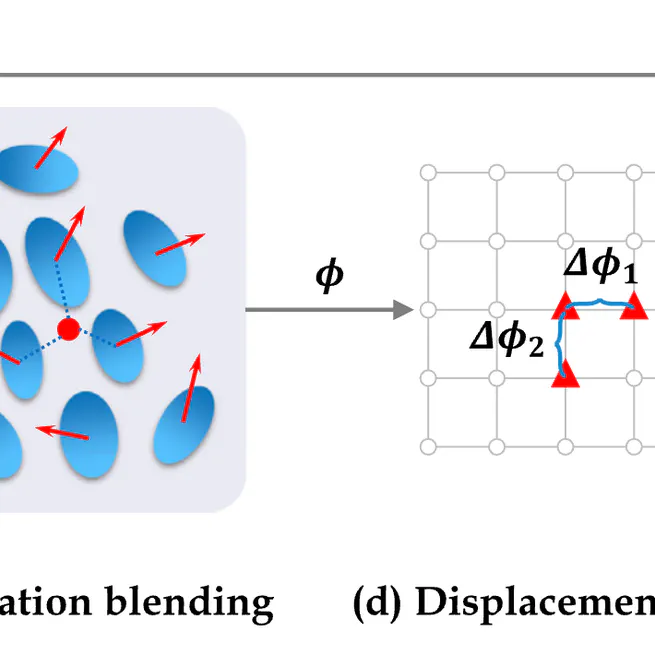
This study presented an optimization-based DIR ap-proach that employed an explicit Gaussian representation to achieveefficient DVF estimation, strong generalization, and high interpretabil-ity.
Jul 9, 2025
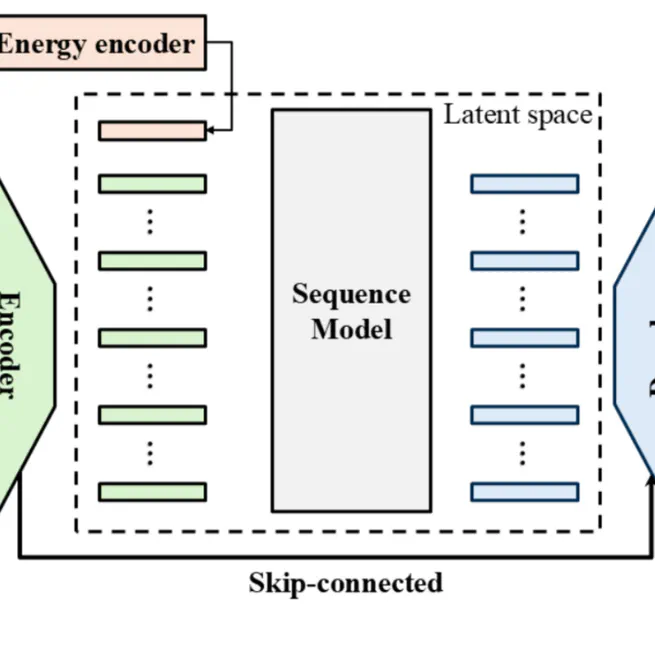
This study demonstrated the feasibility of MC-quality proton dose calculations directly from MR images for brain tumor patients, achieving comparable accuracy with faster computation and simplified implementation.
Jul 5, 2025
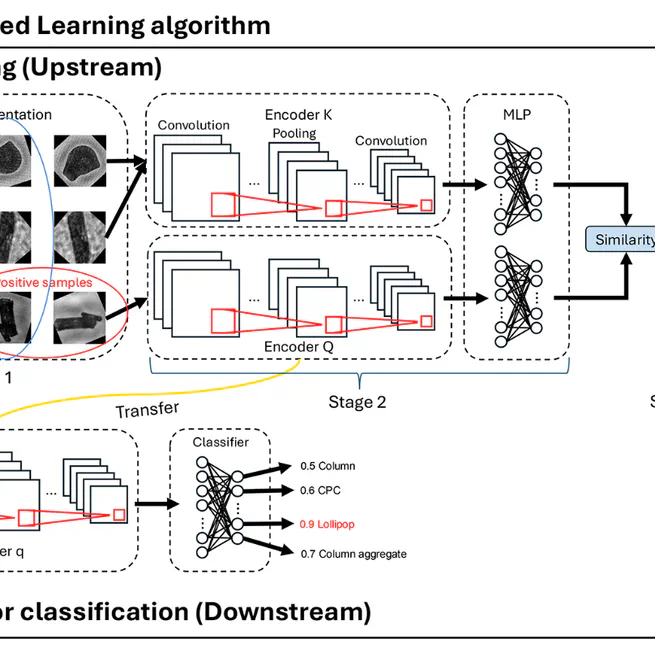
A contrastive semi-supervised learning (CSSL) algorithm for ice crystal classification that reduces manual labeling effort by 90% (154 hours saved) while maintaining high accuracy, achieving 89.6% accuracy with only 25% of labeled data.
Jun 27, 2025
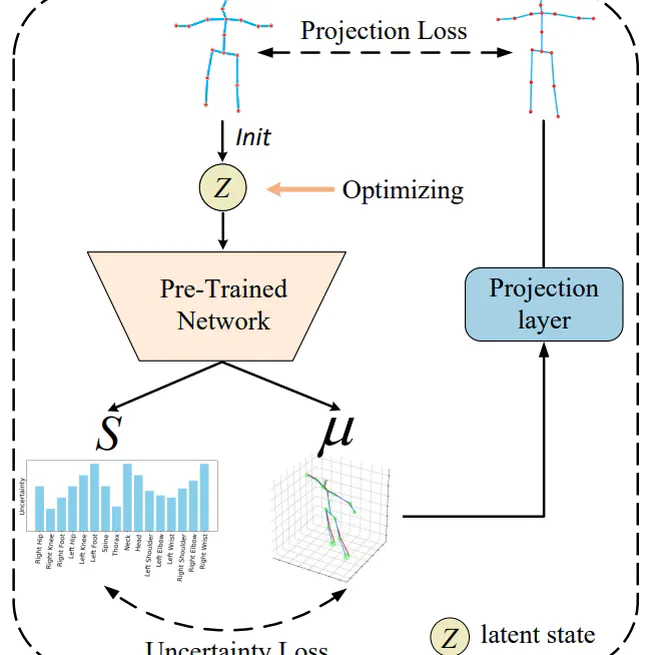
In this paper, we propose an Uncertainty-Aware testing-time Optimization (UAO) framework for 3D human pose estimation. During the training process, we propose the GUMLP to estimate 3D results and uncertainty values for each joint. For test-time optimization, our UAO framework freezes the pre-trained network parameters and optimizes a latent state initialized by the input 2D pose. To constrain the optimization direction in both 2D and 3D spaces, projection and uncertainty constraints are applied. Extensive experiments show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on two popular datasets
Jun 15, 2025
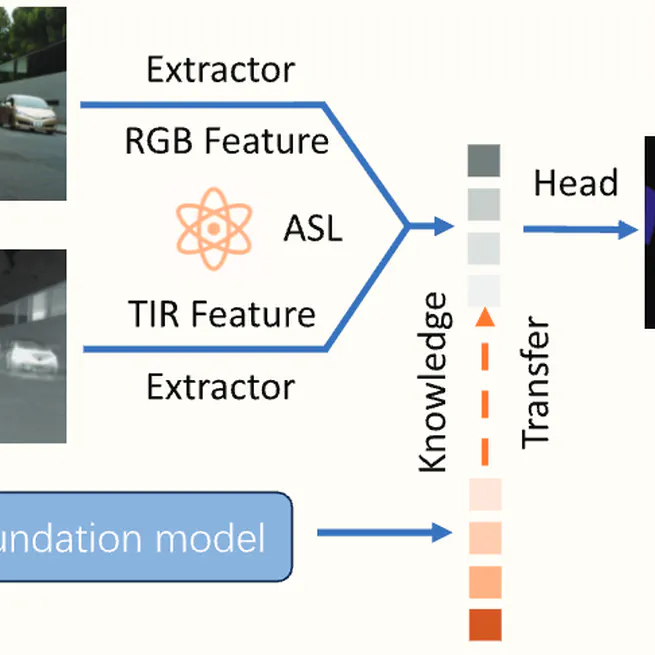
A novel module-free Multiplex Interactive Learning Network (MiLNet) for RGB-T semantic segmentation that integrates multi-model, multi-modal, and multi-level feature learning through asymmetric simulated learning and inverse hierarchical fusion strategies.
Mar 3, 2025
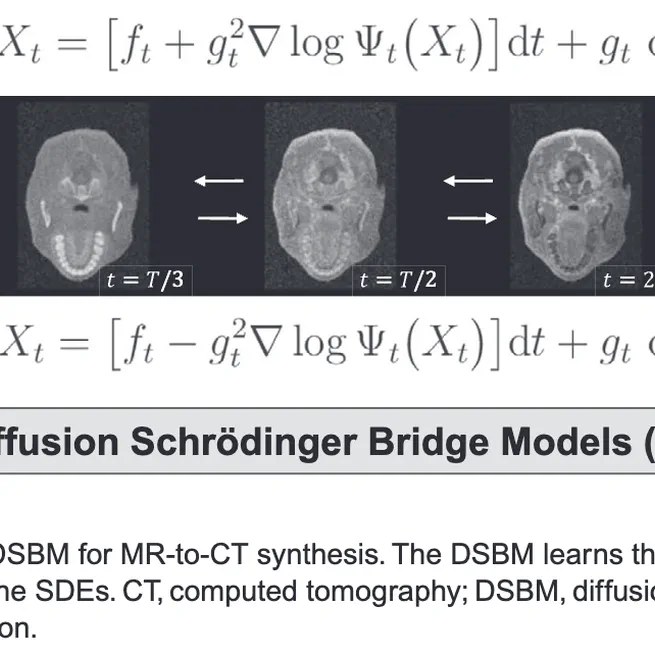
A diffusion Schrödinger bridge model for high-quality MR-to-CT synthesis for proton treatment planning.
Jan 1, 2025
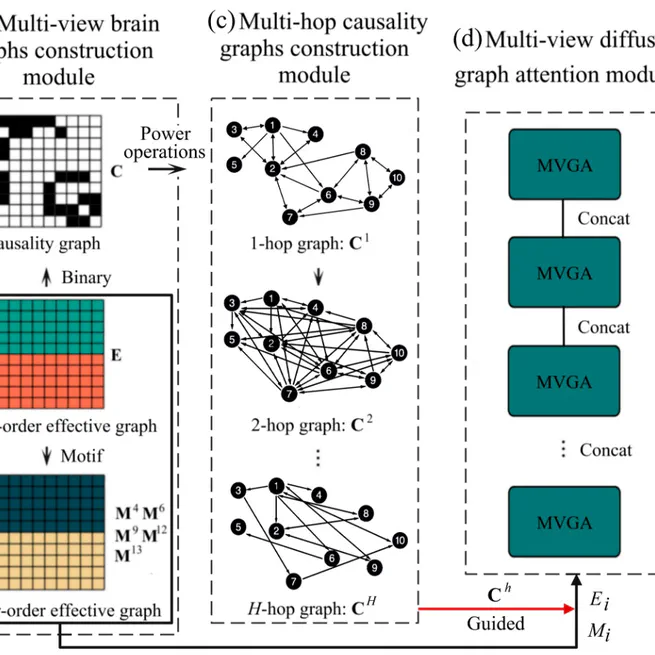
A Prior Causality-Guided Multi-View Diffusion Network (PCMDN) for brain disorder classification that leverages prior causality knowledge and multi-view diffusion processes to improve classification accuracy.
Jan 1, 2025
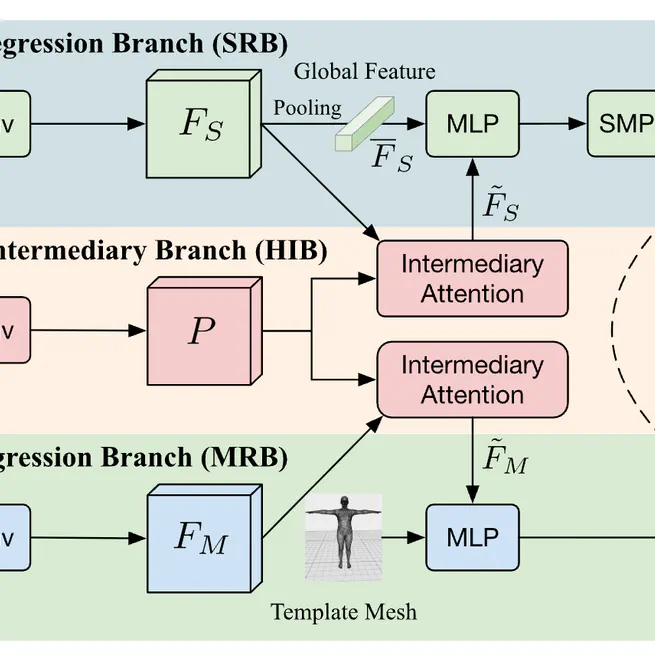
A novel Hybrid Regressor (HYRE) that combines parametric and non-parametric paradigms for 3D human pose and shape estimation, bridging the gap between physically plausible and pixel-aligned results through joint learning.
Dec 25, 2024
A rotated object detection algorithm (IceDetectNet) with a multi-label classification scheme for classifying components of aggregated ice crystals, achieving 92% accuracy for aggregate/non-aggregate detection and 86% for basic habit classification.
Dec 19, 2024
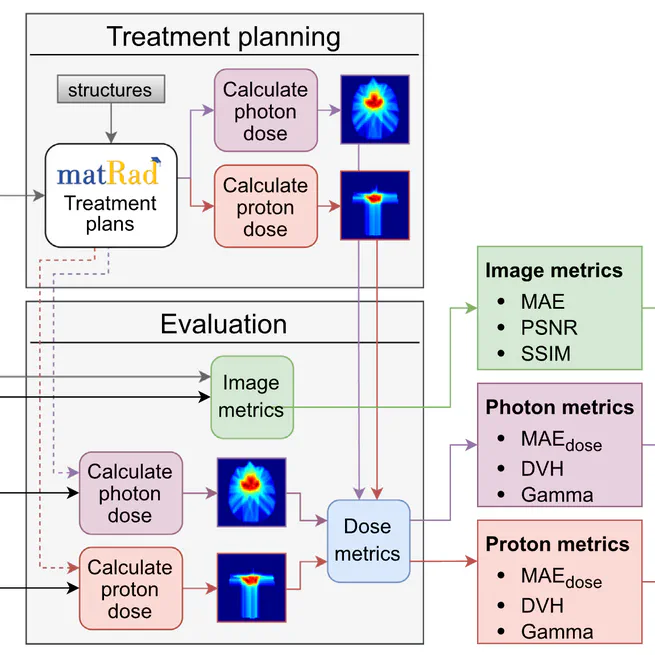
SynthRAD2023 challenge report comparing synthetic CT generation methods for radiotherapy using multi-center data, evaluating both image similarity and dose-based metrics for MRI-to-CT and CBCT-to-CT tasks.
Oct 1, 2024
This study conclusively demonstrates that a holistic MR-based CT synthesis approach, integrating both image-to-image translation and deformable registration, significantly improves the precision and quality of sCT generation, particularly for the challenging body area with varied anatomic changes between corresponding MR and CT.
Aug 13, 2024
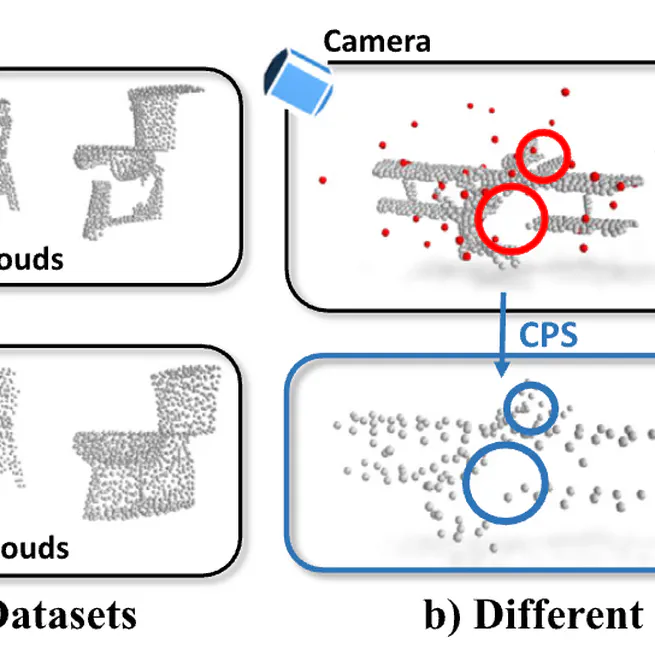
A large-scale synthetic dataset ModelNet-O for occlusion-aware point cloud classification, featuring diverse occlusion patterns and complex object arrangements to evaluate model robustness under occlusion conditions.
Jun 19, 2024
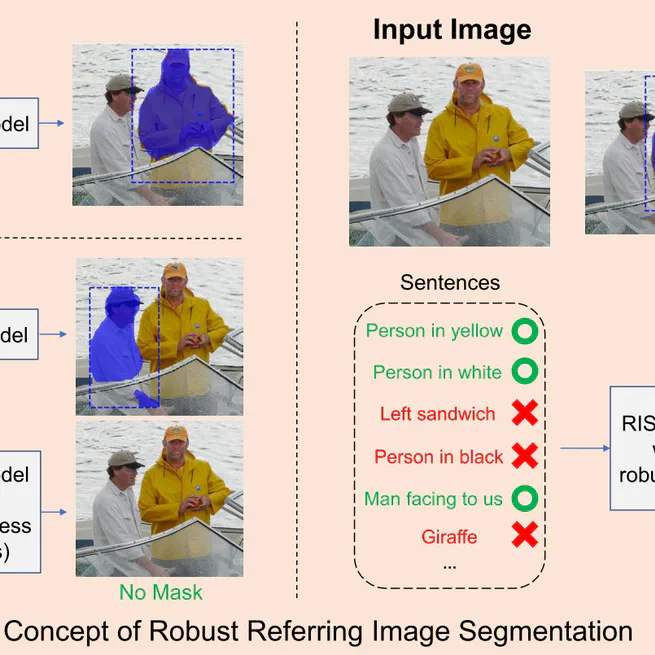
We propose a novel ranking loss function, named Bi-directional Exponential Angular Triplet Loss, to help learn an angularly separable common feature space by explicitly constraining the included angles between embedding vectors.
Mar 5, 2024
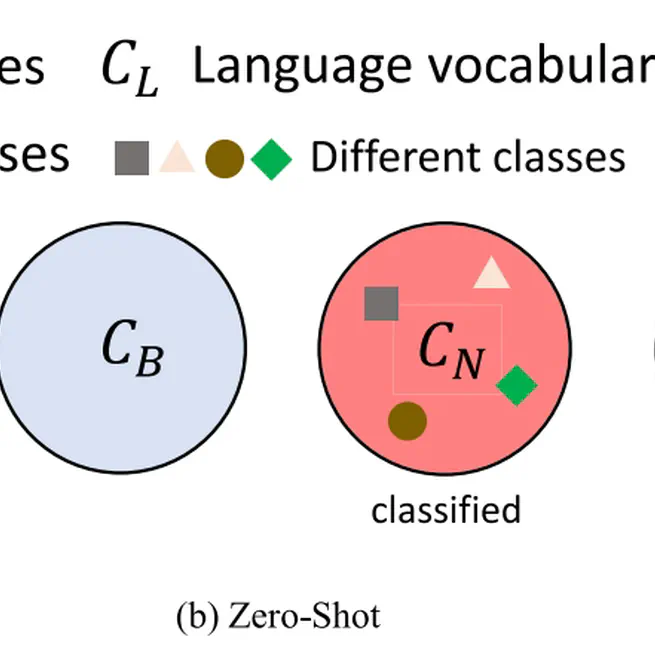
This survey offers a detailed examination of the latest developments in open vocabulary learning in computer vision, which appears to be a first of its kind. We provide an overview of the necessary background knowledge, which includes fundamental concepts and introductory knowledge of detection, segmentation, and vision language pre-training. Following that, we summarize more than 50 different models used for various scene understanding tasks. For each task, we categorize the methods based on their technical viewpoint. Additionally, we provide information regarding several closely related domains. In the experiment section, we provide a detailed description of the settings and compare results fairly. Finally, we summarize several challenges and also point out several future research directions for open vocabulary learning.
Feb 5, 2024
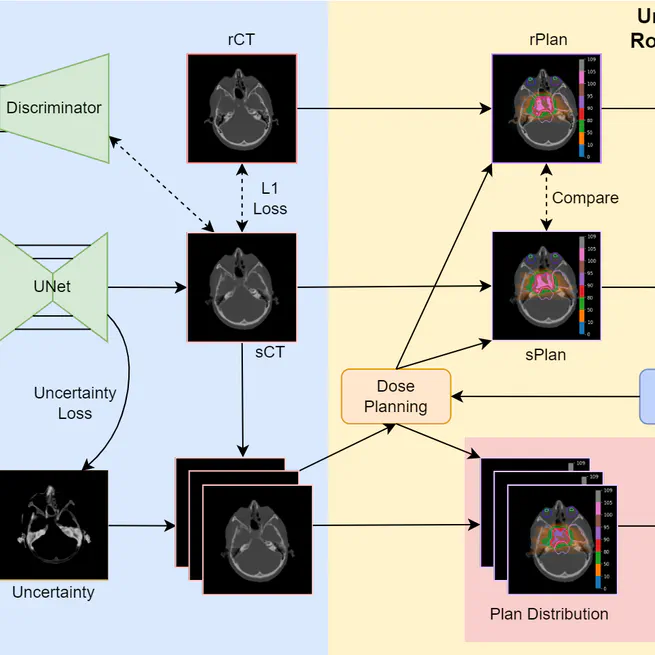
The enhanced framework incorporates 3D uncertainty prediction and generates high-quality sCTs from MR images. The framework also facilitates conditioned robust optimisation, bolstering proton plan robustness against network prediction errors. The innovative feature of uncertainty visualisation and robust analyses contribute to evaluating sCT clinical utility for individual patients.
Feb 1, 2024
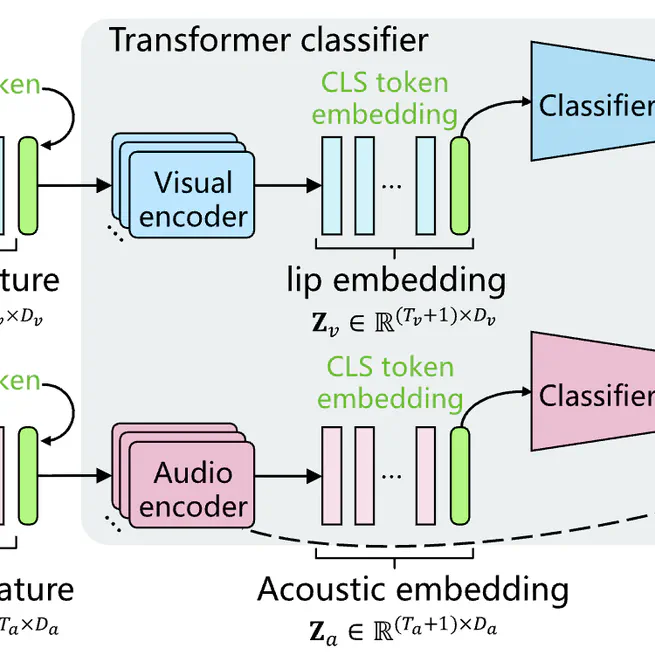
An Audio–Visual Keyword Transformer (AVKT) network for keyword spotting in unconstrained video clips, using transformer classifier with learnable CLS tokens and decision fusion to achieve high accuracy in both clean and noisy conditions.
Feb 1, 2024
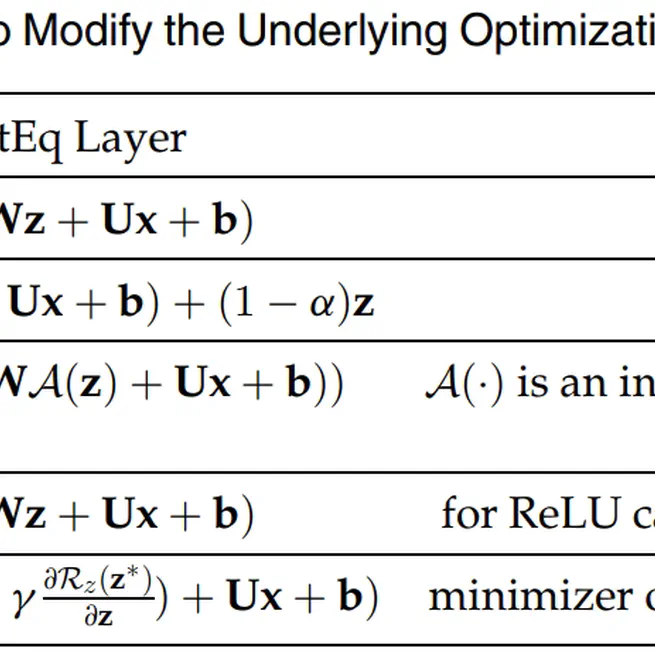
In this paper, we decompose the feed-forward DNN and find a more reasonable basic unit layer, which shows a close relationship with the proximal operator. Based on it, we propose new equilibrium models, OptEqs, and explore their underlying optimization problems thoroughly. We provide two strategies to introduce customized regularizations to the equilibrium points, and achieve significant performance improvement in experiments. We highlight that by modifying the underlying optimization problems, we can create more effective network architectures. Our work may inspire more interpretable equilibrium models from the optimization perspective.
Jun 10, 2022
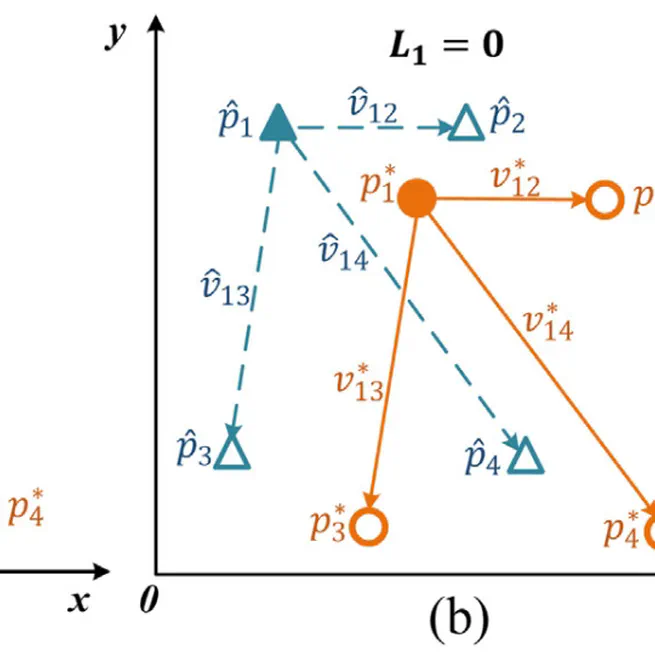
In this paper, we design a Position Constraint Loss (PCLoss) for fashion landmark estimation, which incorporates the position correlation into landmark estimation models. Specifically, the PCLoss adds a regular term for each landmark to regularize their relative positions. Compared with other alternatives, our PCLoss effectively mitigates the outliers and duplicate detection problems without modifying existing CNN architectures. In addition, our skeleton-like optimization method further strengthens the position constraints between landmarks. The proposed method can be applied to both regression and heatmap based methods and it provides a novel perspective towards position relation learning in key point estimation tasks. Extensive experimental results on three challenging datasets, DeepFashion, FLD and FashionAI, demonstrate that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art methods. The experiment on COCO 2017 shows the potential applications of PCLoss for other key point estimation tasks, which can be explored more in future work.
Oct 1, 2021
Jul 30, 2021
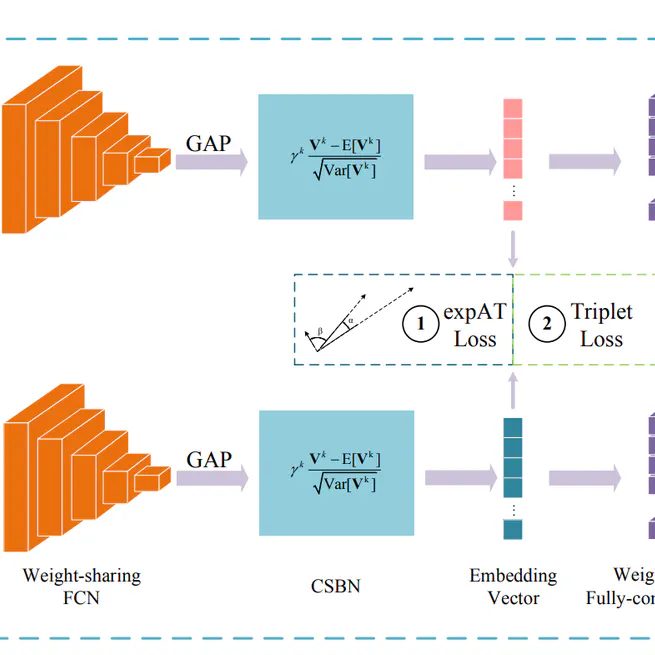
We propose a novel ranking loss function, named Bi-directional Exponential Angular Triplet Loss, to help learn an angularly separable common feature space by explicitly constraining the included angles between embedding vectors.
Dec 12, 2020
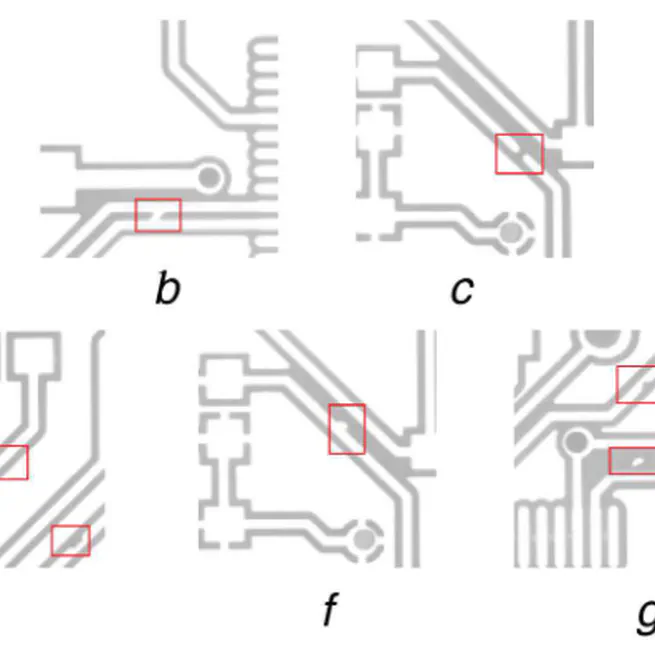
A multi-label classification method based on Convolutional Neural Network for PCB defect detection that can simultaneously identify multiple defect types, improving detection accuracy and efficiency.
Oct 22, 2018